
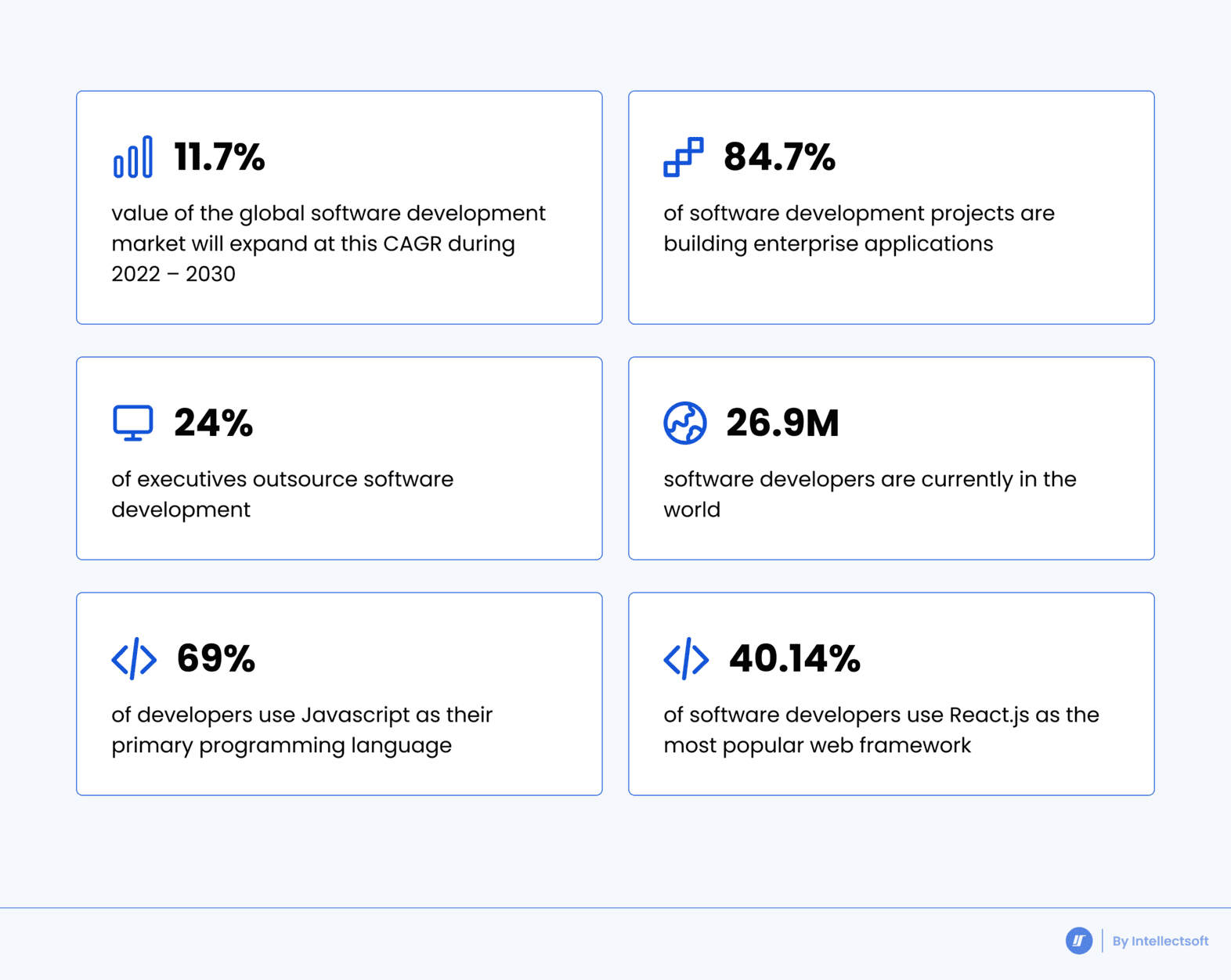
Web Application Architecture: The Basics
Web apps have clearly taken their place in the digital landscape, leading businesses to evolve with cutting-edge technologies and rising safety expectations.
As the web app market stays competitive and the demand for secure solutions increases, considering web app architecture has become more important than ever. This “foundation” of web app development is the backbone of building an app for your business. A thoughtfully designed architecture ensures that your web apps remain responsive, secure, and scalable as your business grows.
In this article, we’ll dive into the components, types, and models of web application architecture. With this knowledge, you’ll be well-equipped to confidently choose the right web app architecture for your needs. Keep reading to learn more!
What is a web architecture?
The definition of web app architecture is broad and depends on the focus of your web applications. At its core, a web application architecture is a model that defines how the components of a web app interact with each other. For instance, a client-server architecture, where the client is the user interface and the server is the back-end, is a common model. The choice of architecture is closely tied to how the application logic is distributed between the client and server sides.
Technically, it’s the intricate skeleton of a web app, encompassing its elements, databases, systems, servers, interfaces, and all the communication happening between them. More abstractly, it indicates the complex logic behind responses to client and server requests.
When it comes to business benefits, web application architecture plays a keyl role in building web applications and planning for their needs, ensuring they deliver on speed, scalability, security, and other key quality attributes.
Components of Web Application Architecture
As the applications differ in complexity and functionality, the number of layers and components changes accordingly. In some cases, an app is simple enough to work as a monolith, storing all the web application design architecture in one place.
However, most web apps consist of multiple components, or tiers, that interact with each other. Typically, web application architecture is divided into two major groups: user interface and structural web components. Structural web components, in turn, include both client-side and server-side components.
When numerous components are involved, descriptions alone might not clearly understand the entire system. This is where a web application architecture diagram comes in handy, offering a visual representation of the components and their interactions. Let’s take a closer look at the key elements shown in this diagram.
.
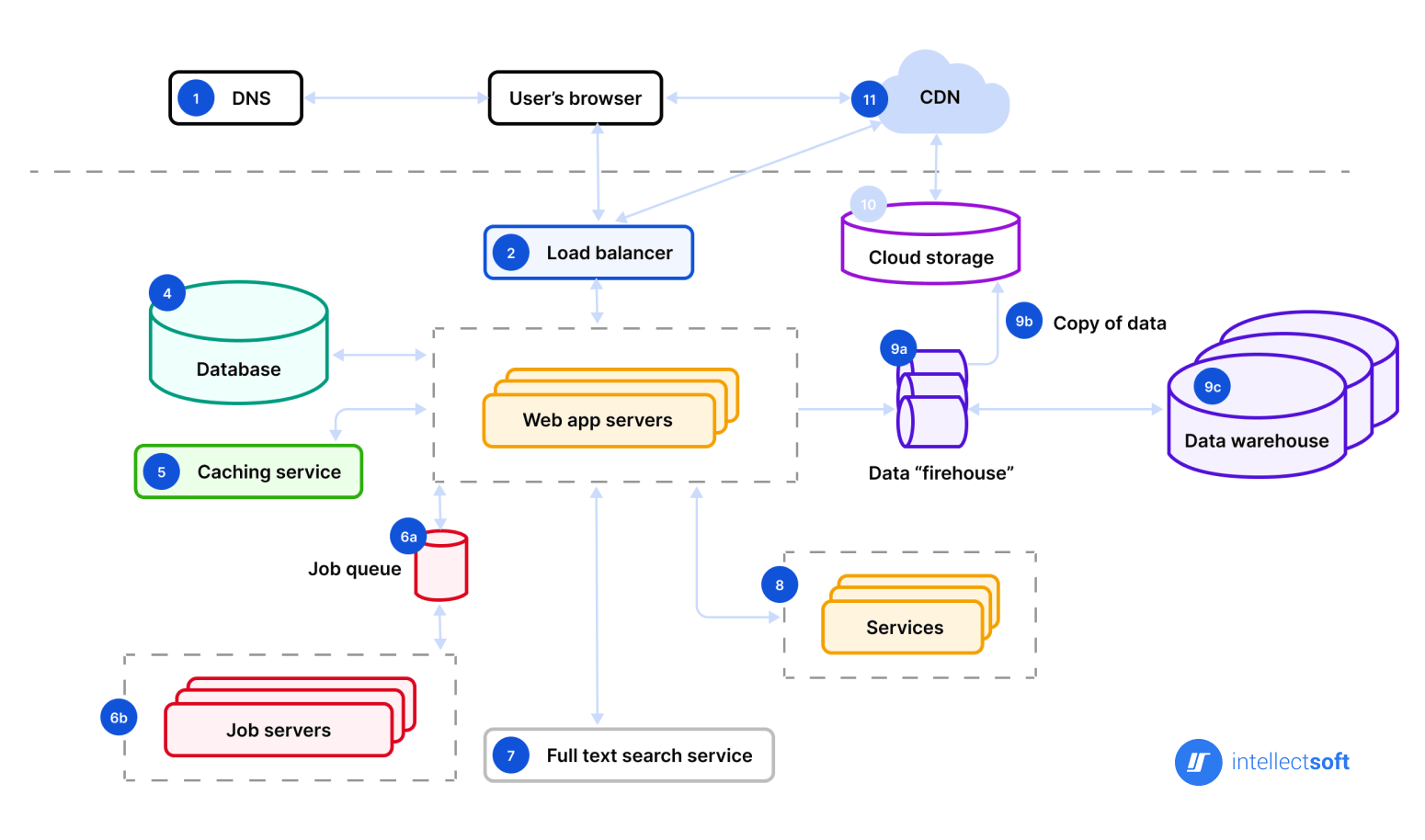
DNS
The abbreviation DNS stands for the domain name system. It’s a key element that matches IP addresses to domain names. In this way, a particular server receives a request sent by an end user.
Load Balancer
It directs incoming requests from app users to one of the multiple servers, which distributes the load more evenly when too many users are active at the same time. Generally, web app services exist as various copies mirroring one another to enable all servers to process requests in the same manner. Also, the load balancer is an element that distributes tasks to prevent them from overcharging.
Web App Servers
This component is basically an app deployment descriptor. It processes the user’s requests and sends responses back to an initial browser. To make this happen, it refers to the back-end infrastructure, including the database, job queue, cache server, etc.
Database
The meaning of this component is pretty much straightforward. It offers various instruments to perform, delete, organize, and update data entries. Mainly, web app servers interact with job servers without any intermediary.
Caching Service
The component grants easy and quick data storage and search. When the user receives the info from the server, search results can be cached. As a result, future requests will be returned much faster.
These are the scenarios when caching is efficient:
- Slow or repeated computation
- When a user receives similar results for a specific request
Job Queue (Optional)
This one has two components: a job queue and servers that process those jobs. Many web servers operate a large number of jobs of minor importance. A job that has to be fulfilled goes in the queue and will be operated according to the schedule.
Full-Text Search Service (Optional)
There are plenty of web apps that support search by text feature. After this, an application sends the relevant results to an end user. The whole process is called a full-text search, and it can find the requested data by a keyword among all the documents available in a system.
CDN
The abbreviation CDN stands for the content delivery system. This system sends static content, including images and other files. Basically, it includes multiple servers that are closer to the geographical locations of end users than an app’s database. As a result, CDN delivers content more effectively to users around the globe, drastically reducing load times.
What is a 3-tier Architecture?
The majority of web apps are created through the separation of their principal function into layers/tiers. Respectively, this enables you to quickly and effortlessly replace or upgrade those layers independently. It is called a multi- or a 3-tier architecture.
In a 3-tier web architecture, there are three layers/tiers:
- Presentation (client) layer
- Application (business) layer
- Data access layer
It’s possible to say that this modern web app architecture is the safest and most secure one. It can be explained by the fact that the client doesn’t access the data directly. Application servers can be deployed on multiple machine providers, which enables higher scalability, increased performance, and better efficiency.
Each tier can be scaled independently; therefore, this architecture can be scaled horizontally. In addition, it also significantly improves the overall data integrity as data will go through the app server, which is the one that decides exactly how and by whom data will be accessed. This fantastic perk is an easy and cost-effective solution in case of new company management.
Modern Web Application Architecture Layers
Now, let’s take a closer look at each of the three web application architecture layers.
Presentation/Client Layer
When we talk about the presentation layer, we refer to the front end of an app. This layer includes such elements as static content and dynamic interface that are visible to end users. The environment of this layer is any browser. Among the technologies that are used in this case, we can name HTML, CSS, or JavaScript. The potential frameworks to choose from include Angular, React, and Vue.
Business/Application Layer
Speaking of the business layer, which is also referred to as the application layer, is a part of the app back-end. The web app’s back-end determines business logic and responses to browser requests that are sent to the presentation layer. It consists of the core application logic and outlines all internal flow for data and requests. In this case, servers, serverless cloud platforms, or PaaS are the most convenient environments. Among the programming languages that are used in this case, we can name C#, JavaScript, Java, Python, and PHP. The potential back-end frameworks to choose from include ASP.NET, express.js, nest.js, Spring, Flask, Django, and Symfony.
Data Access Layer
The final layer in this architecture is the data access layer, which plays a crucial role by closely interfacing with the business layer, retrieving essential information from the servers. Simultaneously, the data service layer acts as an intermediary, effectively segregating the business logic from the client side during request processing.
It is an app back-end part that contains databases and DBMS (database management systems) that collect, manage, and store data. The environment can be the same as the application layer. Among the Database management systems, we can name PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, MongoDB, Cloud Offerings, and so on.
All the layers work independently and communicate with each other through the relevant components.
Types of Web Application Architecture
A web application architecture type is a particular pattern under which the components interact with each other. The overarching layers might be divided into client-side architecture, server-side architecture, and a hosting approach.
Client Side
Single-Page Application Architecture
This web application architecture is designed to show relevant content only. To make this happen, it first loads the relevant web page and then dynamically updates the representation of its content with the requested information only.
In other words, it doesn’t refer to the server for loading new pages but sends requests for the needed parts of the webpage only.
Single-page applications contribute to smoother performance and a more intuitive user experience.
Pros of single-page app architecture:
- Faster performance
- Improved flexibility of UX
Cons of single-page app architecture:
- Increased testing time
- Possible loss of unsaved progress
- Slower first-load speed
Progressive Web Apps
Thanks to their unique format, progressive web apps are still among the most promising web app trends. They offer a convenient and effective user experience that is available from any browser and device through a shared URL.
Progressive web apps are widely used in entertainment, finance, and eCommerce industries. Their key benefits include lightweight, cost-effectiveness, cross-device nature, ability to attract web traffic, and a fully functioning app experience.
Pros of progressive web app architecture:
- Browser availability
- Mobile-first approach
- Increased traffic
- Effective offline performance
Cons of progressive web app architecture:
- Restricted browser support
- Narrow utilization of native APIs.
Server Side
Microservice Architecture
Microservices are the frequent alternative to an unreliable monolithic web application architecture. They disperse the functionality to deliver small and lightweight services separately.
In particular, they are loosely coupled and use APIs for communication if a sophisticated business problem arises. This peculiarity eases the developer’s life since it’s possible for individual service components to be built in different programming languages.
Thanks to its flexibility and stability, microservice architecture has gained popularity these days, with businesses like Amazon, eBay, and Netflix adopting it for their complex needs.
Pros of microservice architecture:
- Easier scaling up
- Better fault tolerance
- Simple-to-understand code base
- Independent module deployment
Cons of microservice architecture:
- Difficulties with testing and debugging
- Complex deployment
Hosting Approach
Serverless Architecture
In web application development, this type of architecture allows you to outsource both server and infrastructure management to a third-party cloud service provider. This way, a web app logic execution won’t intervene in the infrastructure running.
Choosing a serverless architecture is good for companies that want to delegate server and hardware management to a reliable tech partner and concentrate on front-end development tasks instead.
Also, this web application architecture type allows working on small functions in apps. The service providers that assist in server management are Amazon and Microsoft, among others.
Pros of serverless architecture:
- Absence of server management
- Highly scalable
- Minimized latency
- Speed and flexibility
Cons of serverless architecture:
- Security concerns
- High complexity
Advanced & Scalable Web Application Architecture
Digital technologies constantly evolve, creating new possibilities for web applications. As a result, their architecture also evolves to accommodate software to new demands and conditions in business. These days, the challenges in various industries require appropriate actions and implemented measures from software developers. Let’s see what business requirements impact software development most and how specialists can ensure the necessary characteristics of web applications using new trends and a properly designed architecture.
Nowadays, three of the most demanded characteristics of web applications are improved scalability, reliability, and security. Business needs to be sure that custom software is reliable and won’t fail under load or malicious actions. To satisfy these requirements, developers continually enhance software architecture by implementing more advanced technologies and higher standards.
Today, most requirements regarding the scalability and safety of web applications are met with the help of cloud technologies. Web developers extensively use them for two main purposes: advanced storage and delivery of content and smart balancing of traffic load.
Cloud solutions are the most obvious and optimal choice of technologies for the architecture of most business web applications. That’s why a lot of web developers effectively use a wide range of cloud services provided by such IT giants as Amazon, Microsoft, and Google. Today, Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform are essential tools that can be customized for all types of web applications.
Here are a few examples of uses and benefits associated with cloud services implementation in web app architecture.
Data Storage Tools
- Amazon S3
- Azure Cloud Storage
- Google Cloud Storage
Storing web app information in the cloud instead of an on-premise server makes data more accessible regardless of users’ location. Most cloud service providers offer several subscription plans with various volume and traffic load capacities. They ensure your information is kept safe and secure, which is an invaluable advantage for business.
Cloud storage also allows developers to optimize access time for users in target geographic areas. This way, customers or employees using a web application will experience fewer lags. After a web application is released, developers can add new cloud storage units, remove existing ones, and change the service subscription plan. This significantly improves scalability and optimizes app costs depending on the scale of the business.
Load Balancing Tools
- AWS Elastic Load Balancing
- Azure Load Balancer
- Google Cloud Load Balancing
Load balancers ensure the smooth work of a web application even at times of high traffic loads. This type of technology is especially useful for B2C or retail businesses. Usually, such high load periods are predicted and happen on a regular basis, for example, during holiday seasons. However, sometimes, they occur as a result of malicious attacks intended to disrupt the online operations of a particular company. The most common type is DDoS attacks, which can have a devastating impact on any online business. Load balancing technologies help to distribute excess loads across multiple servers using hardware or software components and predefined policies.
Caching and Content Delivery Tools
- Amazon CloudFront
- Azure CDN
- Google Cloud CDN and Media CDN
- CloudFlare
Software developers may implement a caching system in application architecture to optimize data access and improve app performance. Usually, an app cache contains the most frequently or recently requested information. It delivers data to a user device much faster than requesting the same information from a database on an application server.
Depending on the architecture, a web application may have a global cache, a distributed cache, or an in-memory cache. Another widely used technology to handle caching is a content delivery network (CDN). It allows developers to reduce load on an application server by rerouting queries to a CDN server instead.
Web Application Architecture Best Practices
Here, we’ve gathered the top 5 recommendations for business owners to consider while working on web app architecture for their projects and building cooperation with tech partners.
- Think of a proper web application architecture at the earliest stages
Without a comprehensive structure, your application will turn into a labyrinth of messy elements and components that are too hard to handle.
- Don’t copy somebody’s success
The top mistake is picking a web application architecture of a successful company and simply replicating it. In reality, a successful architecture is one that corresponds with your business goals and ideas, not theirs.
- Pay attention to your technical limitations
It’s not always possible to get the best and most successful elements in your web application architecture. However, with the proper attention to quality attributes and realistic business expectations, you will get the maximum from all the components you have.
- Eliminate the problems right away
Don’t wait for the web app release to fix the problems in its architecture. The earlier you address the issues, the more reliable core features it will have.
- Create a checklist of successful web app features
To make sure your web app has achieved its goal, it’s good practice to note your expectations from the very beginning and discuss their possibility and measurable KPIs with your tech partner.
The possible checklist may include these features:
- System flexibility
- Reusable components
- Well-written code
- Scalability
- System stability
- Bug detection ease
- Adherence to security standards
- Fields for user feedback
- Crash prevention
- Ease of use
- Fast response
- Automatic deployment
Summing Up
A solid, fast-working, scalable, and safe web application architecture is necessary for every web platform-based digital product, especially for business. For this reason, it’s advisable that the architecture is developed and implemented by software engineering experts with experience in building similar solutions tailored to your specific industry.
Intellectsoft has been creating digital solutions for companies of all sizes in Fintech, Healthcare, construction, hospitality, logistics, eCommerce, and many other industries for over 17 years. We provide web development services to startups, SMBs, and enterprises worldwide and create solutions with the most efficient, safe, and flexible web app architecture.
So, if you’re looking for a development team that will ensure top-quality modern web application architecture, here are only a few reasons to choose our software engineering experts:
- Our talent pool covers dozens of programming tools and technologies for building web, mobile, desktop, cloud, and other solutions.
- We have successfully delivered over 600 digital solutions for businesses. Here, you can see our most prominent cases.
- Our engineering workforce is located in 21 countries across the Atlantic.
- The size of our clients varies from early-stage startups to Fortune 500 enterprises like Audi, Harley Davidson, Universal, Nestle, Melco, and others.
If you’re ready to explore the custom web application architecture we can create for your business, don’t hesitate to contact us. Our team will ensure your product has the perfect modern web app architecture.

